WACV 2025 (Best Student Paper)
GeoDiffuser: Geometry-Based Image Editing with Diffusion Models
1 Brown University
2 Amazon Robotics
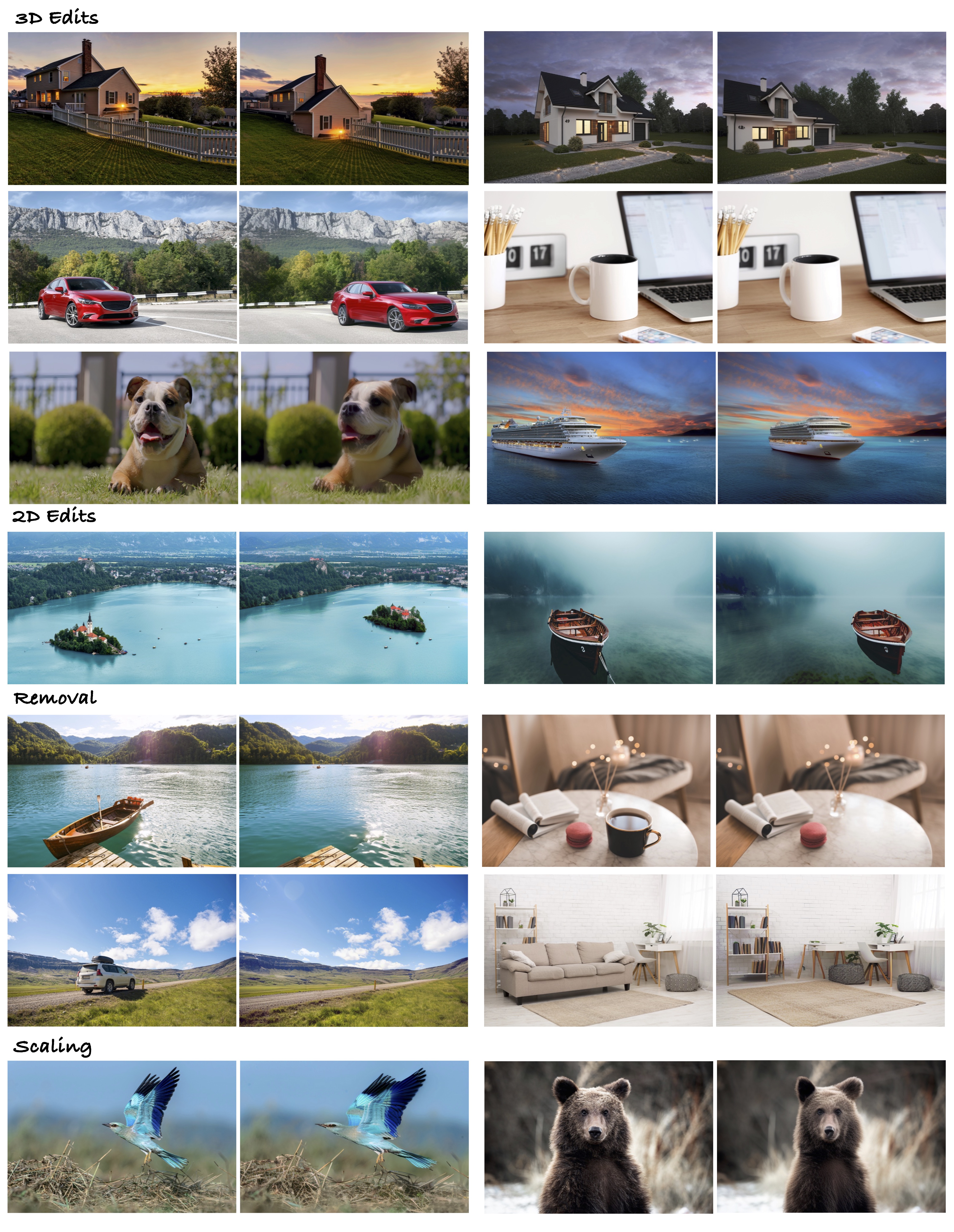
Real Image Editing with GeoDiffuser
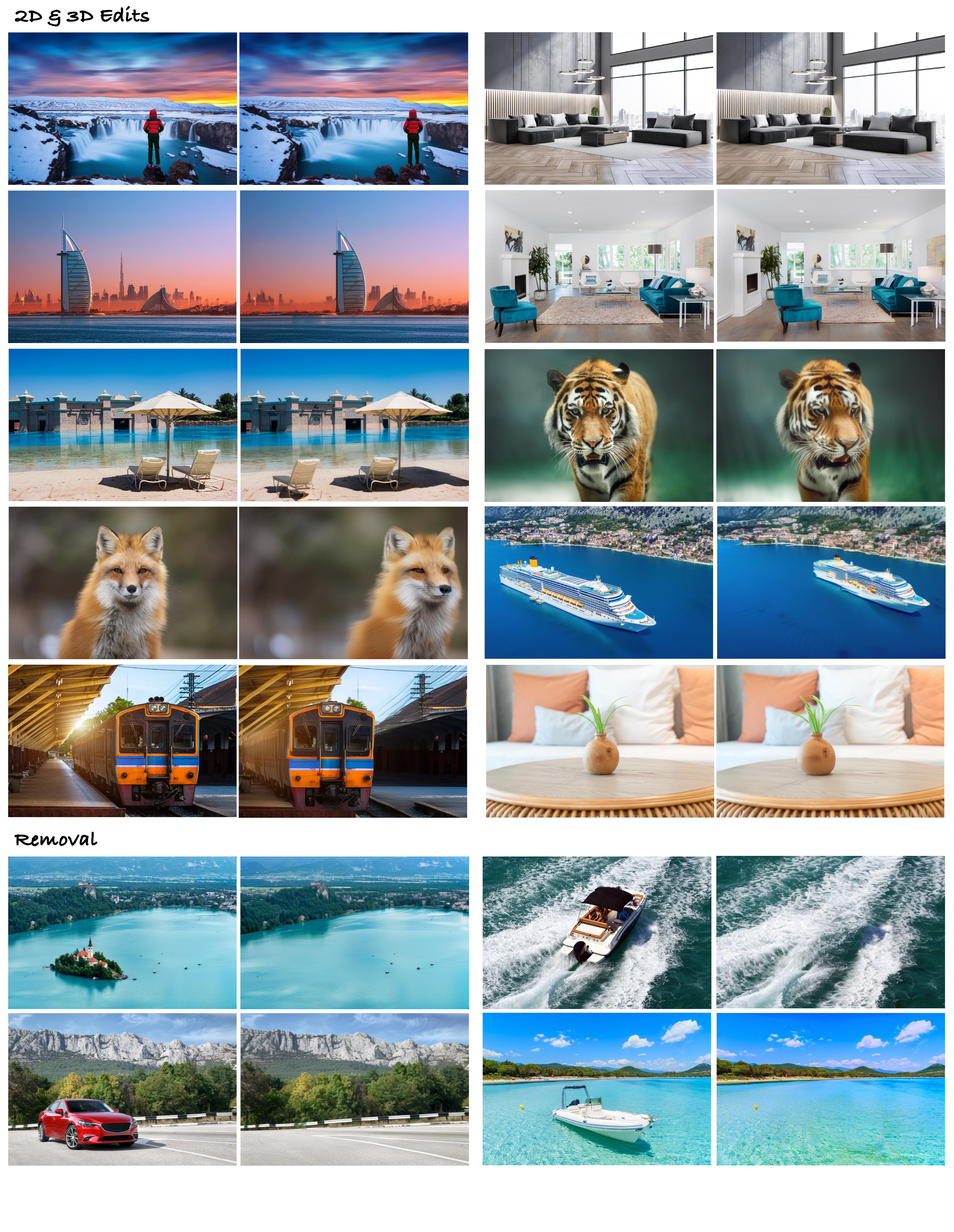
2D and 3D Edits












Object Removal
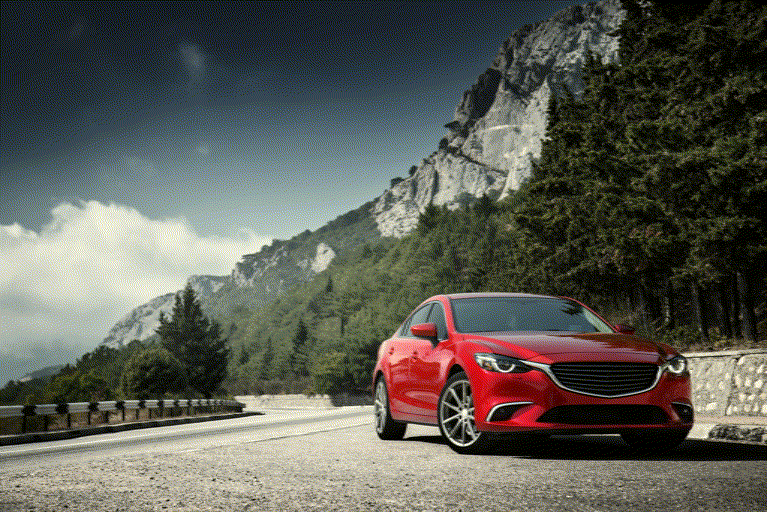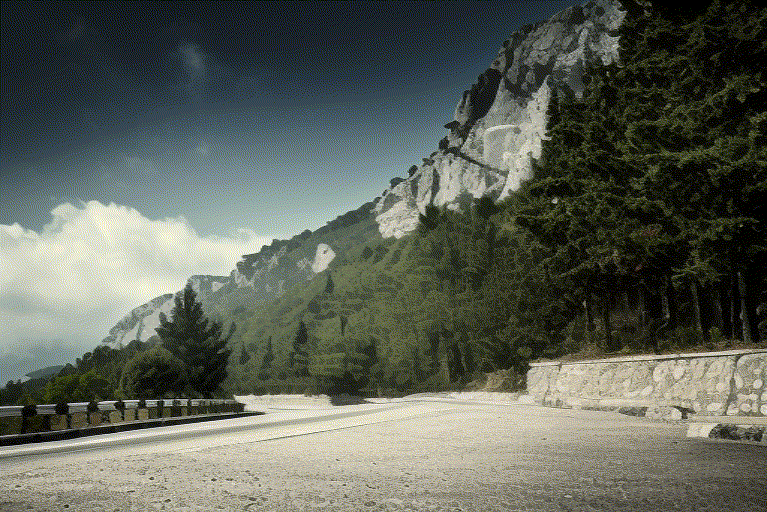



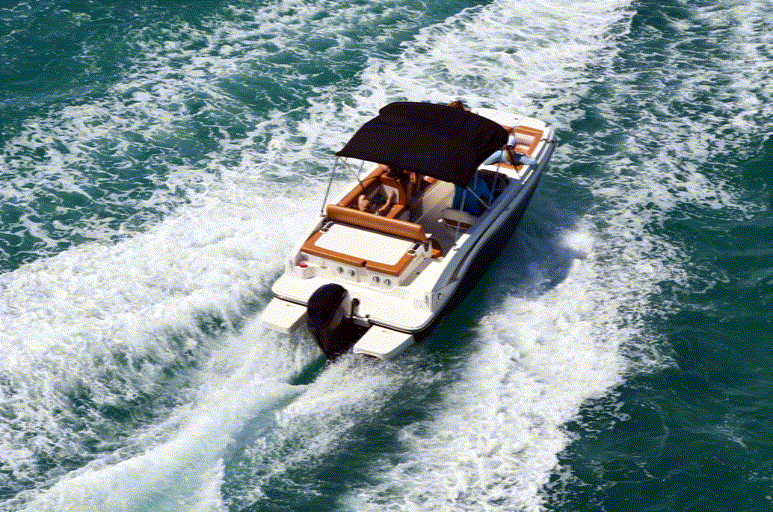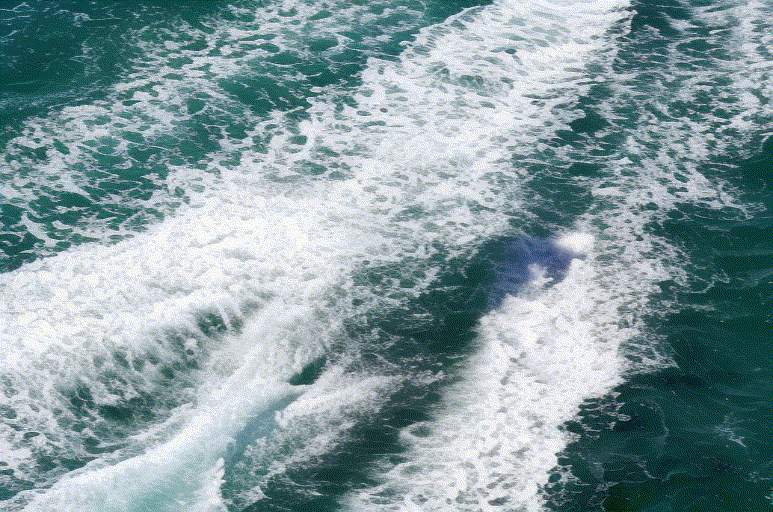

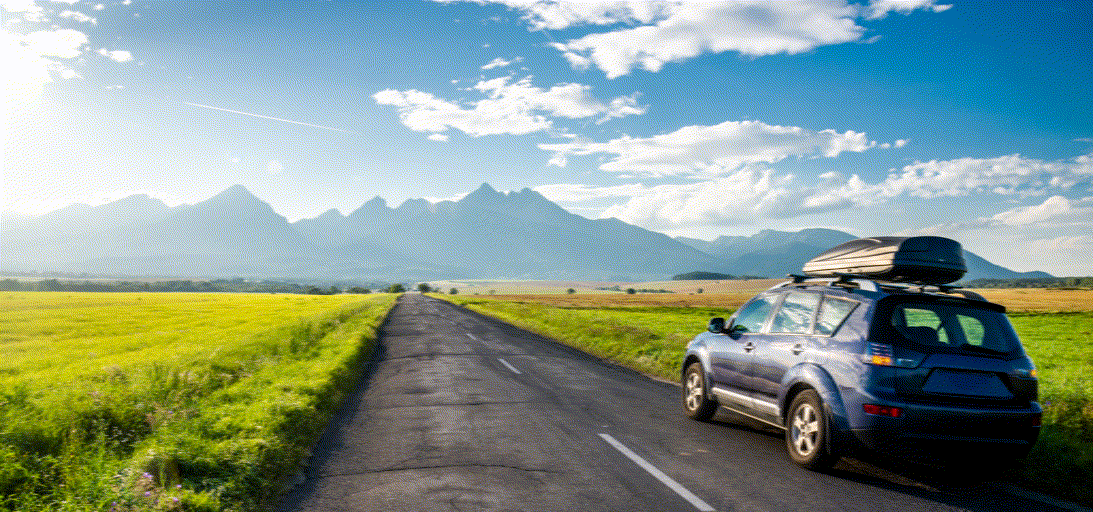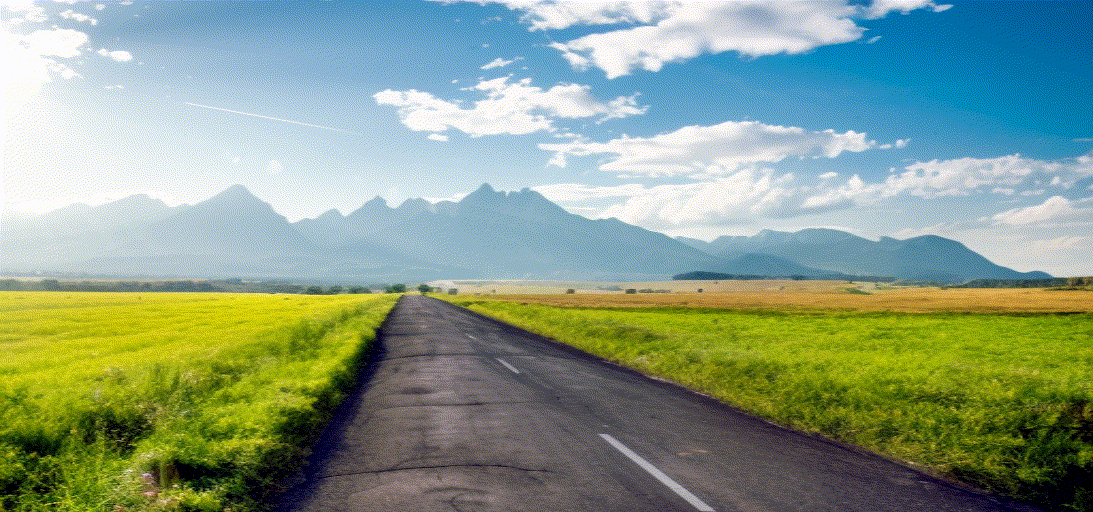

Overview

The success of image generative models has enabled us to build methods that can edit images based on text or other user input. However, these methods are bespoke, imprecise, require additional information, or are limited to only 2D image edits. We present GeoDiffuser, a zero-shot optimization-based method that unifies common 2D and 3D image-based object editing capabilities into a single method. Our key insight is to view image editing operations as geometric transformations. We show that these transformations can be directly incorporated into the attention layers in diffusion models to implicitly perform editing operations. Our training-free optimization method uses an objective function that seeks to preserve object style but generate plausible images, for instance with accurate lighting and shadows. It also inpaints disoccluded parts of the image where the object was originally located. Given a natural image and user input, we segment the foreground object using SAM and estimate a corresponding transform which is used by our optimization approach for editing. GeoDiffuser can perform common 2D and 3D edits like object translation, 3D rotation, and removal. We present quantitative results, including a perceptual study, that shows how our approach is better than existing methods.
General Editing Framework
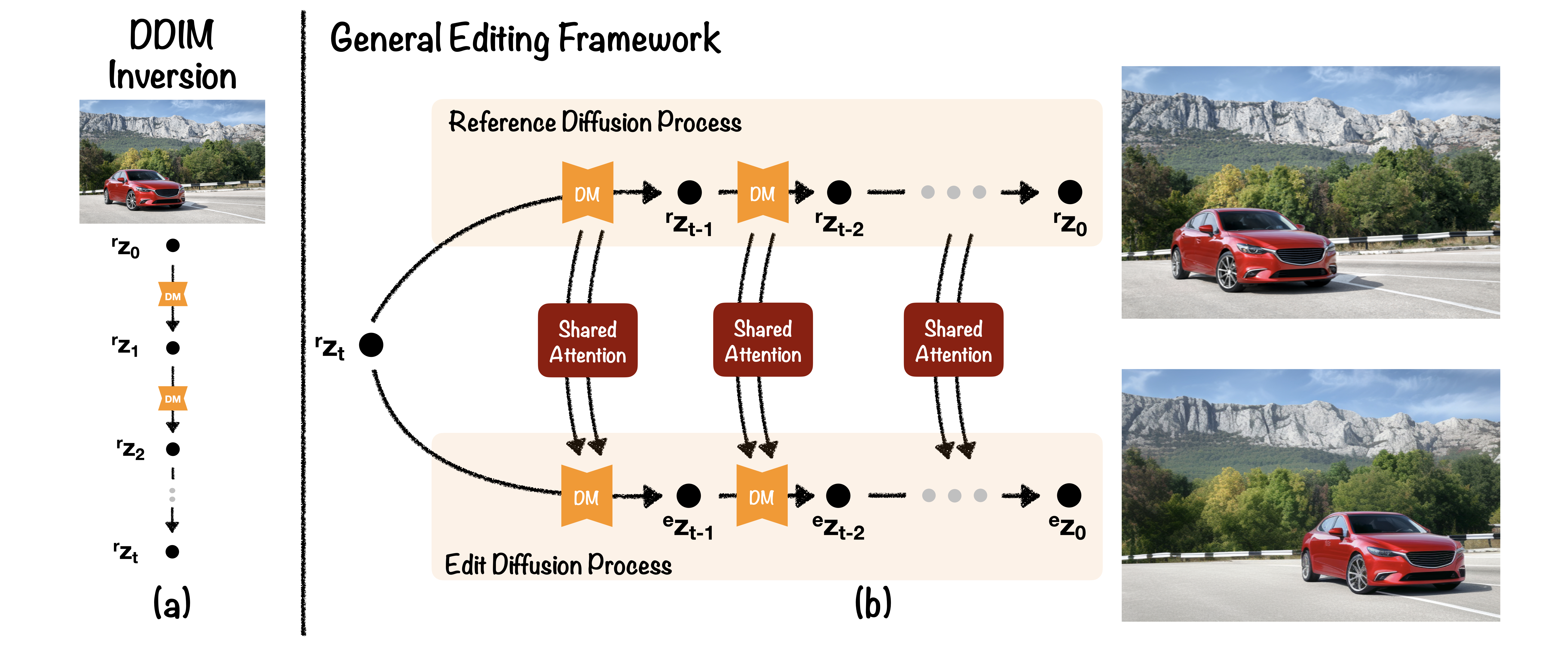
Prior works leverage the learned capabilities of diffusion models to perform edits to a given image, rather than a generated one. A general framework (see Figure 2) that is followed in all prior editing works is to first perform an inversion on the image. This inversion provides us with a noise latent that sets a good starting point to regenerate the input image as well as to edit it. Starting from the inverted noise latent, two parallel diffusion processes generate the input image as well as the edited image. The reference diffusion process generates the original input and, in our work, helps preserve un-edited regions of the image. An edit diffusion process runs in parallel that utilizes the attention blocks from the reference process to perform the desired edit. This shared attention is a key insight for our proposed work. The editing framework is in Figure 2 (b).
Method Overview
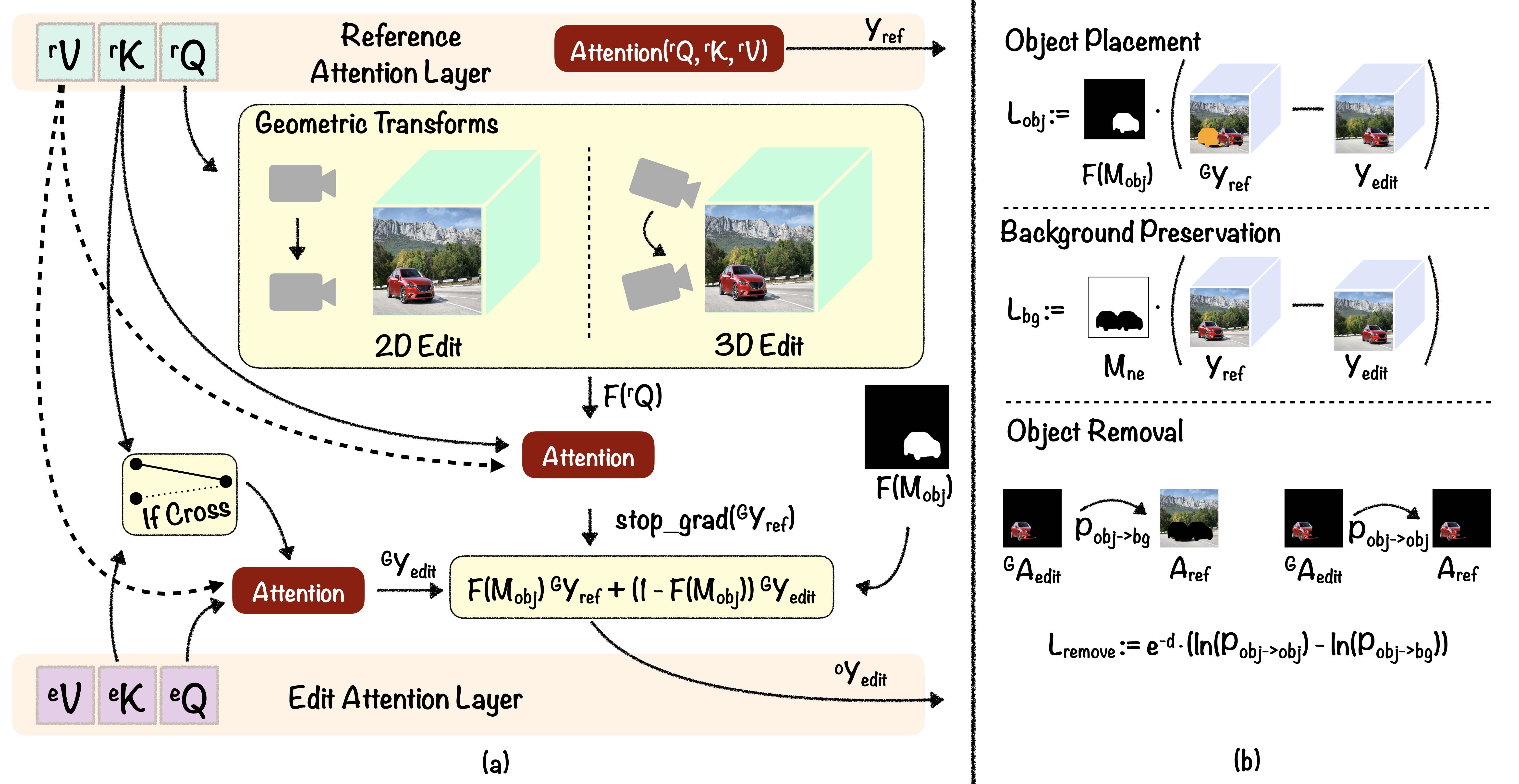
GeoDiffuser proposes a novel attention sharing mechanism that performs both 2D and 3D geometric edits within the attention sharing layer (shown in Fig.3 (a)). Our approach is a zero-shot optimization-based method that operates without the need for any additional training. We achieve this via optimization of the latents for edit guidance. The shared attention guidance provides us with a proxy of where the foreground object must be placed after the edit. We formulate an optimization procedure for the latents, in order to fill in the disocclusions and penalize the deviation of the edit attention guidance from the reference attention guidance. The loss functions are used to penalize the diffusion latents in the optimization (shown in Fig. 3 (b))
Results
Limitations
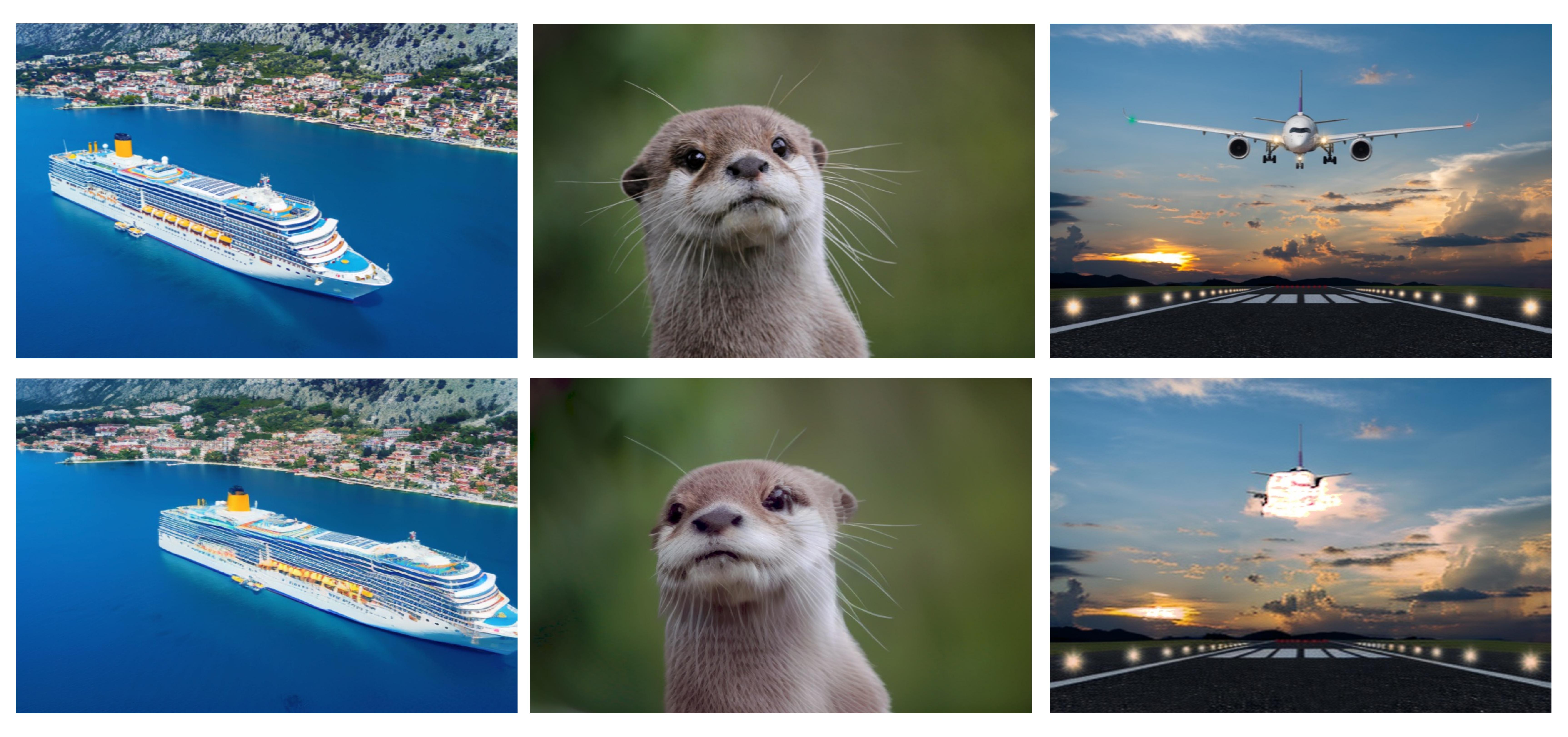

Each example presents the input image at the top followed by the edited image at the bottom. As our geometric edits are performed in a lower dimensional latent space, we face aliasing and interpolation artefacts as shown in the yellow regions of the ship (left). Occasionally our optimization results in sub-optimal solutions for foreground (middle) and background dis-occlusions (right)
Citation
@misc{sajnani2024geodiffuser,
title={GeoDiffuser: Geometry-Based Image Editing with Diffusion Models},
author={Rahul Sajnani and Jeroen Vanbaar and Jie Min and Kapil Katyal and Srinath Sridhar},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.14403},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was done during Rahul’s internship at Amazon. This work was additionally supported by NSF grant CNS #2038897, ONR grant N00014-22-1-259, and an AWS Cloud Credits award.
Contact
Rahul Sajnani rahul_sajnani@brown.edu